The Printing Methods Guide
Posted by Clash Printing Atlanta on 27th Sep 2023
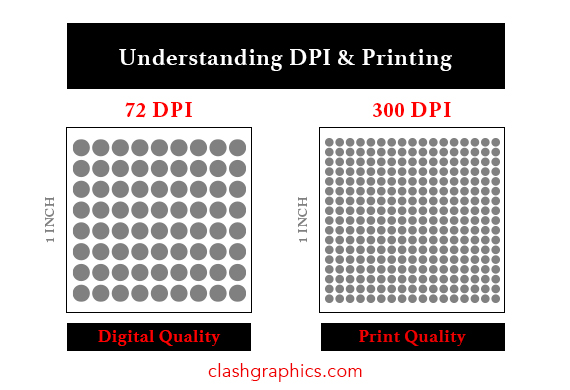
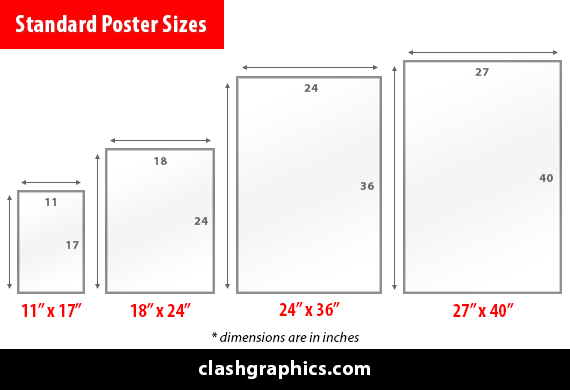
In today's fast-paced world, the art of printing has evolved along with technology to meet the diverse needs of various industries. From creating vibrant promotional materials to crafting intricate 3D models, printing methods have come a long way. In…
read more