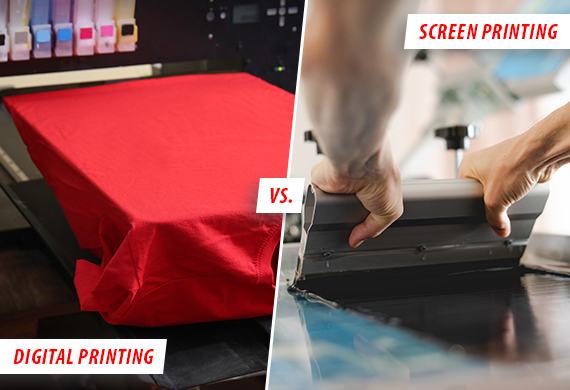
Digital Printing vs Screen Printing
Posted by Clash Printing Atlanta on 28th Dec 2023
In the vibrant world of printing, the age-old battle between traditional screen printing and modern digital printing rages on. But which method reigns supreme? Is it the time-tested craft of screen printing with its rich, vivid colors and lasting durability? Or is it the cutting-edge digital printing boasting high-speed production and incredible detail accuracy? Unearth the answers and gain a fresh perspective as we dive into this intriguing debate: digital printing vs screen printing.
Key Digital vs Screen Print Takeaways
Screen printing is a traditional method of printmaking that produces vibrant, durable designs on various materials and fabrics.
Digital printing offers quick production, precise output, and high-quality uniform prints.
Factors to consider when choosing between digital and screen printing include the number of items, design complexity, cost & desired print locations.
Understanding Screen Printing
Delving into screen printing takes us back to the roots of printmaking. This ancient method, dating back to the early Egyptian civilizations and later refined in China around 900 A.D., eventually evolved into a commercial process in the 1880s. Today, it remains a popular choice for its ability to create vibrant, durable designs on various materials, from textiles and plastic to latex, making it ideal for items such as balloons, clothing, and wallpaper.
Screen printing distinguishes itself with its unique capacity to yield designs that burst with vibrancy. Unlike other apparel printing methods, such as Direct-To-Garment (DTG) digital printing, screen printing is renowned for bringing colors to life, making them stand out in stark contrast to their backgrounds. This versatility can be attributed to the plasticity of the ink and the capability to manually operate and control the process, allowing for flexibility in printing on various objects.
The Screen Printing Process
Uncovering the nuances of the traditional screen printing process, we find a method rich in tradition and technical accuracy. To bring a design to life, ink is forced onto the printing surface through a stencil, with each color necessitating a separate screen. This stands in contrast to digital printers, which directly print the image onto the surface without the need for stencils or screens.

Screen printing, also known as screen print, is particularly suited for:
Large, simple designs that do not require intricate detail
Designs that need to be correctly aligned
Various fabrics, including t-shirts, jackets, and even canvas shoes - making it a popular choice among screen printers.
The tools and materials used in screen printing include:
Screen tape
Ink spatula or scoop
Platen adhesive
Squeegees
Screen
Stencil material
Registration plastic
Water-based screen-printing inks
Digital non-contact laser thermometer
The process, including setup, job registration, and printing, typically takes around 15 minutes per shirt, with drying times varying depending on the ink type.
Advantages of Screen Printing
Despite screen printing appearing more laborious than digital printing, it brings numerous advantages that make it a strong competitor. Screen printing stands out for its use of vibrant Plastisol and water-based inks, resulting in the most vivid colors. It also enables the creation of various special effects, including:
raised print
texture
shine
sparkle
glow
Very bright neon colors can be achieved through the use of specialty inks and additives. This attribute is unique to the screen printing method.
When it comes to large orders, screen printing is the undisputed champion. Due to its ability to preserve color vibrancy and special effects even on a large scale, it's the go-to method for high-quantity orders, providing cost-effectiveness that digital printing can't match.
Additionally, screen printing showcases notable versatility, providing the capability to print on diverse textiles, different garment styles, and various print locations that digital printing can't replicate.
Unraveling Digital Printing

Moving into the domain of digital printing, we step into an environment marked by speed, precision, and adaptability. Unlike screen printing, digital printing uses digital technology to print directly onto various surfaces, such as T-shirts, employing digital files and inkjet technology. Introduced in the late 20th century, digital printing has quickly risen to prominence due to its rapid production, precise output with minimal preparation, and high-quality prints.
Digital printing is particularly favored when absolute uniformity in the final output is essential. It is commonly employed for direct mail, coupons, or materials that demand a contemporary, sharp appearance. The primary categories of digital printing are roll printing and flatbed printing, each catering to different needs and project sizes. The versatility of digital printing, combined with its high-quality output, has made it a popular choice for many, especially those seeking speed, accuracy, and detailed prints.
The Digital Printing Process
Going further into the digital printing process, we observe its main strength is its simplicity and speed. It all begins with the transmission of a digital file to a digital printer that employs inkjet technology to have the image printed directly onto the garment, eliminating the necessity for intermediary steps like stencil or screen creation. This method, known as direct-to-garment printing, showcases the efficiency of the digital printing process.
At the heart of this process is the CMYK color model, a widely accepted digital printing standard combining four primary colors—cyan, magenta, yellow, and black—to produce diverse colors. Some advanced printers may incorporate extra colors, such as red and green, to expand the color gamut.
Digital printing can support various types of materials, including paper, textiles such as cotton, wool, and silk, and non-textile surfaces like acrylic, plastic, and cardboard.
Advantages of Digital Printing
The advantages of digital printing are as manifold as the colors it can generate. One of its standout features is its capacity to accurately reproduce detailed patterns and images, as well as its exceptional color blending capabilities that create seamless gradients and a diverse spectrum of colors.
In terms of cost, digital printing shines for small order quantities due to its low setup fees, eliminating the high initial costs associated with creating screens and stencils for screen printing, thus making it cost-effective for small runs. Furthermore, digital printing maintains consistent quality across prints by utilizing a computer-controlled digital setup to control ink distribution at a consistent rate for each piece, ensuring uniformity across all printed items.
Comparing Costs: Screen vs. Digital
The scenario becomes evident when surveying the cost dynamics of these two printing methods: screen printing is generally more cost-effective for large quantities due to its cheaper printing speed for high volumes. Conversely, digital printing, which has low or non-existent setup fees, is more cost-efficient for small orders. The average cost for screen printing is approximately $5 to $10 per unit, while digital printing typically ranges from $1 to $4 per unit.
However, the cost-effectiveness of each method isn't just about the price tag. It's also about the quality of the final product. While screen printing may offer a lower cost per unit for large quantities, it's also important to consider the longevity and vibrancy of the prints - translating into greater value over time.
Setup Fees and Time
Looking into the specifics, we discover that setup fees and time play notable roles in determining the cost-effectiveness of each printing method. Screen printing necessitates allocating resources for creating screens and stencils, which incurs setup fees. The typical cost of setup fees can vary from $20 to $50 per color, and the process generally involves approximately 10 minutes for setting up a screen printing job, with the duration contingent upon the intricacy of the design and the number of colors involved.
In contrast, digital printing offers efficiency for smaller orders due to the absence of setup fees and quicker setup, making it cost-effective and time-saving for small quantities compared to screen printing. The absence of these fees significantly reduces the cost for small orders compared to screen printing.
Price Per Print and Quantity
Regarding the price per print, the scales tip in favor of screen printing as the number of items to be printed increases. The price per unit for screen printing generally decreases as the number of shirts ordered increases, as this is a commonly employed pricing strategy by many print shops.
However, in the world of digital printing, the cost per unit remains constant regardless of the quantity of the order. The cost remains consistent throughout the print run, making it an attractive option for smaller orders where the quantity might not be large enough to offset the initial setup costs of screen printing.
Design and Detail Considerations
In deciding between digital and screen printing, your design's characteristics hold significant weight. Screen printing is more suitable for uncomplicated designs and high volumes, whereas digital printing is particularly effective for intricate designs and gradient patterns.
The choice of method can greatly influence the outcome of your print quality. Screen printing is more suited for bold graphics, large shapes, and text-based designs. In contrast, digital printing shines when it comes to reproducing files with a high level of detail, such as photographs, and maintaining high color accuracy.
Complex Designs and Gradients

When it comes to complex designs and gradients, digital printing takes the lead. It can accurately replicate detailed gradients, shading, and complex color blends, ensuring seamless transitions without visible bands of color. This makes it ideal for reproducing files with a high level of detail, such as photographs, while maintaining high color accuracy.
However, screen printing is not left entirely in the dust. It's capable of handling gradients and finely detailed images through the use of halftones or greyscales. While it can replicate photographs and complex illustrations, it may not achieve the same level of detail and color gradients that are as smooth and effortless as in digital printing.
Simple Designs and Large Quantities
Screen printing plays to its strengths when it comes to simple designs and large quantities. It provides benefits such as vivid colors and efficient production of large amounts, making it a cost-effective option for uncomplicated designs that do not necessitate intricate details or a wide range of colors.
This is especially evident when manufacturing larger volumes, as the input costs are spread across more items, lowering the overall cost per item. Screen printing is the way to go when the design is simple and the quantity large.
Durability and Material Compatibility

While cost and design elements are important, durability and material compatibility hold equal significance in comparing screen and digital printing. Screen printing provides superior durability compared to digital printing. Digital prints may deteriorate with washing, particularly in hot water, whereas screen printing if done correctly, will maintain its color and vibrancy for an extended period.
Each method also has its own set of material compatibilities. Screen printing is compatible with a wide range of materials, including fabric, paper, plastic, metals, polymer films, textiles, and latex, making it suitable for diverse applications. On the other hand, digital printing is ideal for natural fabrics like cotton, silk, and wool and tends to perform best on 100% cotton or other natural fabrics.
Adhesion and Weather Resistance
When it comes to adhesion and weather resistance, screen printing's sturdy nature takes the spotlight. The greater adhesive quality of screen printing ink can be attributed to its historical ability to adhere to a wider range of surfaces, including glass and aluminum. The thicker ink layers in screen printing facilitate improved adhesion to the substrate, and the ink can also form a mechanical bond with the fabric, further enhancing its adhesion. Using a fine mesh screen ensures the final product's precision and durability.
On the other hand, digitally printed designs may face issues such as mottled prints, slower drying times in high humidity, and potential fading from U.V. exposure, indicating lower weather resistance than screen printed designs. Furthermore, varnish coatings, U.V. coatings, and protective coatings are necessary for digital prints on certain materials.
Material Compatibility

Each method presents its unique strengths and limitations in terms of material compatibility. Screen printing is compatible with materials such as:
cotton
polyester
tri-blend fabrics
cardboard boxes
tote bags
wood
However, it's primarily focused on polyester-based materials, reducing its versatility and requiring water-based inks with their own fabric limitations and a shorter shelf life.
In contrast, digital printing accommodates a broader spectrum of fabrics, including:
silk
canvas
fabric
polyester
paper
card stock
cotton
viscose
wool
polyamide
lycra
mixed fabrics
However, it's subject to constraints such as size limitations caused by the printing equipment and compatibility issues with specific materials such as certain plastics or synthetic papers that may not effectively absorb or adhere to the ink, resulting in adhesion issues that affect quality.
Making Your Decision: Factors to Consider
Standing at the junction between digital and screen printing, several pivotal factors demand your consideration. The most appropriate method for your project will depend on the following:
The number of items to be printed
Design complexity
Cost
Desired print location on the apparel or item
Fabric color
The number of colors in the design
For example, if you're a business owner looking to print a large quantity of t-shirts with a simple, bold design, screen printing would likely be the most cost-effective choice.
On the other hand, digital printing with a local print shop may be the way to go if you're an artist looking to reproduce a complex, detailed design on a smaller quantity of items. The decision ultimately depends on your individual needs and the specific requirements of your project.
Summary
Ultimately, the choice between screen and digital printing isn't a matter of which is objectively better but which is better suited for your specific needs. Both methods have their strengths: screen printing, with its vibrant colors and cost-effectiveness for large quantities, and digital printing, with its precision detailing and cost-effectiveness for small quantities. Consider the factors we've discussed – quantity, design complexity, cost, print locations, fabric color, and the number of colors in your design – to make an informed decision that will best serve your project. Remember, the perfect print isn't about the method but how well it brings your vision to life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is digital printing or screen printing better?
Digital printing is better for smaller orders that need to be individualized and have complex designs, while screen printing works best for higher quantities of simple designs with less color gradients.
What is digital printing good for?
Digital printing is excellent for producing small print runs of detailed artwork in a shorter timeframe and at a lower cost per unit.
What is the difference between screen printing and digital textile printing?
Screen printing offers a more vibrant finish, while digital textile printing provides better detail due to thinner layers of ink.
Why is digital printing more expensive?
Digital printing is more expensive due to expensive equipment, single-use paper, special ink, and a costlier printer. As the quantity of prints increase, so do the time and cost of digital printing equipment, supplies, and operation.
How does the durability of screen printing compare to digital printing?
Screen printing is generally more durable than digital printing, with vibrant colors that last longer.
(678) 235-3464